The Reasons Non-Alcoholics Are Also at Risk for Liver Disease# The Reasons Non-Alcoholics Are Also at Risk for Liver Disease Alcohol use is frequently one of the first things that comes to mind when we think of liver damage. But it’s important to understand that heavy drinking is not the only cause of liver damage. Not only is it false to assume that alcohol is the sole cause, but it can also be harmful to people who ignore other risk factors. The purpose of this essay is to dispel this misconception and examine the different ways that people who do not drink may also be at risk for liver disease.
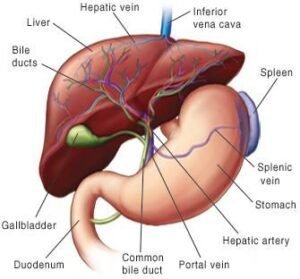
## Comprehending Liver Disease We must first examine what liver disease is in order to comprehend why non-alcoholic people can develop it. The liver is a big, important organ that is essential for digesting nutrition, metabolizing drugs, and filtering pollutants. Damage or dysfunction of the liver, which can come from a number of sources, is referred to as liver disease.
- Liver illnesses come in a variety of forms, including but not restricted to:
- **Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
- ** 2. **Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
- ** 3. **A, B, and C hepatitis
- **4. **Autoimmune Liver Diseases
- ** 5. **Genetic Disorders (such as Wilson’s Disease or hemochromatosis)
- ** ## Fatty Liver Disease Without Alcohol (NAFLD) NAFLD is one of the most common liver conditions among nondrinkers. Contrary to popular belief, a sizable portion of the population suffers from this ailment, particularly individuals who have high cholesterol, diabetes, or obesity.
- ### Why Do People Get NAFLD? A significant risk factor is obesity, particularly central obesity, which is characterized by the buildup of fat around the belly.

NAFLD - **Insulin Resistance**: Frequently associated with diseases such as metabolic syndrome and Type 2 diabetes.
- **Unhealthy Eating Practices**: Diets heavy in processed foods, refined sugars, and saturated fats cause the liver to swell with fat. A sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. It is concerning to note that non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe form of NAFLD, can develop into cirrhosis, fibrosis, and even liver cancer.
- ## Hereditary Conditions and Genetics is another important factor that contributes to liver disease in non-alcoholic people. A person may be more susceptible to liver issues if they have certain genetic disorders.
- ### Some Instances: **Hemochromatosis**: A hereditary condition that causes the body to accumulate iron excessively, which damages the liver.
- **Disease Wilson’s**: Copper builds up abnormally in this disorder, which can lead to liver and other organ failure. A uncommon condition known as **Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency** causes low amounts of the protective protein alpha-1-antitrypsin, which can result in liver and lung damage.

Hepatitis Viral Regardless of alcohol consumption, viral diseases such as hepatitis A, B, and C can potentially cause liver damage. Because they can develop into chronic conditions and result in long-term liver problems, hepatitis B and C are especially significant. **Hepatitis B**: Spread by coming into contact with bodily fluids that are contagious, hepatitis B can cause chronic liver disease if left untreated. **Hepatitis C**: Usually spread by blood-to-blood contact, hepatitis C can cause persistent liver infections that, if left untreated, can cause serious liver damage over time.
# Toxins and Medicines Environmental pollutants and drugs also have an unanticipated impact on liver health in non-alcoholic people. Liver damage can result from the overuse or abuse of drugs like acetaminophen, even at small dosages over time. Environmental exposure to specific chemicals and poisons can also be detrimental.