Liver at Risk: How Alcohol Abuse Causes Lasting Damage
Though many consume it globally, few understand the terrible effect it may have on one of your most vital organs—the liver. Although sometimes drinking might not appear bad, persistent alcohol misuse can result in permanent harm that could even endanger life.
This all-encompassing book will cover how alcohol impacts the liver, the phases of alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), important indicators to look out for, and methods to avoid permanent damage.
What Makes the Liver So Important?
Located on the upper right side of your belly, the liver is a huge, football-sized organ. Among its more than 500 essential tasks are:
Eliminating dangerous chemicals (like alcohol)
Making bile for digesting
Controlling cholesterol and blood sugar
Manteniendo vitaminas y minerales
The liver is on the front lines when you drink since it is the body’s cleansing center. Still, it has its limits.
How Does the Liver React to Alcohol?
Tu hígado descompone el alcohol cuando lo consumes, utilizando enzimas como la alcohol deshidrogenasa (ADH) y la aldehído deshidrogenasa (ALDH). Ethanol (alcohol) is transformed by this technique into the extremely hazardous chemical acetaldehyde; finally, it becomes innocuous water and carbon dioxide.
Your liver, though, struggles to keep up if you drink often or heavily. Over time, acetaldehyde and other hazardous byproducts accumulate, harming liver cells and causing scarring and inflammation.
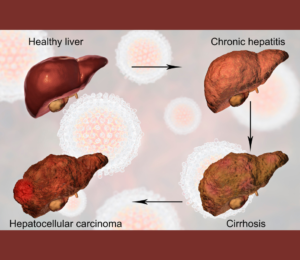 Stages of Liver Disease Related to Alcohol
Stages of Liver Disease Related to Alcohol
Usually, alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD) advances in three main phases. Knowing these phases will enable you to identify early warning signals and look for assistance before it is too late.
1. Alcoholic Steatosis (Fatty Liver)
What exactly is it?
The most prevalent and early kind of ARLD is fatty liver. Excessive alcohol useleads to the accumulation of fat in liver cells, which in turn causesg fatty liver.
Signs:
Usually symptomless
Occasionally slight upper right abdominal pain
Can it be reversed?
Absolutely! Stopping drinking early enough will allow fatty liver to completely reverse.
Hepatitis from alcohol
What exactly is it?
Inflammation of the liver tissue brought on by ongoing alcohol misuse is called alcoholic hepatitis. This stage might be minor or severe; in certain instances, it appears unexpectedly.
Indications:
Yellowing of the skin and eyes defines jaundice.
Vomiting and nausea
High temperature
Stomach ache
Decreased hunger
Can it be reversed?
While severe alcoholic hepatitis could be life-threatening and cause lifelong liver damage, mild cases can go better with abstinence.
Cirrhosis
What is it exactly?
The most severe stage of cirrhosis is defined by significant liver scarring. This scarring destroys good liver tissue; hence, it permanently compromises liver function.
Indications:
Excessive weariness
Leg and abdominal swelling (ascites)
Simple bleeding and bruises
Memory issues or confusion (hepatic encephalopathy)
Skin spider-like blood vessels
Can it be undone?
Sadly, most of the time cirrhosis is irreversible. A liver transplant could sometimes be the sole choice in advanced situations.
The Science Underlying Alcohol-Related Liver Damage
Acetaldehyde The Quiet Assassin
The major consequence of alcohol metabolism, acetaldehyde, is a carcinogen harming liver cells directly. It causes scarring and inflammation, hence paving the way for long-term liver damage.
Oxidative pressure
Heavy drinking increases the production of free radicals, unstable chemicals harming DNA, proteins, and cells. Oxidative stress from this speeds up liver damage.
Liver-Gut Axis
Alcohol compromises the intestinal barrier, letting bacterial toxins—like lipopolysaccharides—leak into the circulation. Reaching the liver, these chemicals cause further inflammation and aggravate liver damage.
Causes of Alcoholic Liver Disease
Heavy drinkers do not all suffer major liver damage. Your risk is affected by several things, including:
Your risk increases the more and longer you consume alcohol.
Women are more prone than males to liver disease connected to alcohol.
Genetics: Certain individuals have hereditary differences that increase their susceptibility.
Worsens alcohol-related liver damage and raises the likelihood of fatty liver.
Viral hepatitis: Alcohol increases the damage in coexisting hepatitis B or C infections.
How Much Is Too Much Alcohol?
Health recommendations say:
Men: Daily maximum of two standard drinks
Women: No more than one standard drink each day
One standard drink is:
5% alcohol in 12 oz (355 ml) of beer
Five ounces (148 ml) of wine (12% alcohol)
1.5 oz (44 ml) of 40% alcohol spirits
Consistently going beyond these boundaries increases your risk for ARLD.
Early Warning Signs to Look Out For
Liver disease is difficult since it usually quietly progresses in the early stages. Look out for:
Ongoing weariness or weakness
Skin/eye yellowing (jaundice)
Weight reduction without cause
Abdominal or leg swelling
Loss of appetite or queasiness
Should you see any of these symptoms, please see a doctor right away.
Diagnosis of Liver Damage Related to Alcohol
To identify liver impairment, doctors combine several techniques:
Blood tests: to monitor clotting factors, bilirubin, and liver enzymes (AST, ALT).
Imaging: MRI, CT, or ultrasound to assess the state of the liver.
Fibroscan/Elastography: Indicates fibrosis or cirrhosis by measuring liver stiffness.
In some situations, a little tissue sample is collected for further analysis.
Is the liver able to heal?
Among the few organs that can heal is the liver. Complete healing is feasible within weeks to months if alcohol usage is halted early—particularly during the fatty liver or mild hepatitis stages.
Once major scarring, or cirrhosis, sets in, the damage is generally irreversible. Even then, avoiding alcohol can stop more development and enhance quality of life.
Choices for Treatment
1.Abstinencia de alcohol
Stopping alcohol consumption totally is the first and most important action. Your liver health will be greatly improved by this one act, which will also help to avoid problems.
2.Nutritional Assistance
People with ARLD frequently suffer from malnutrition. Liver recovery is supported by a balanced diet high in proteins, vitamins, and minerals.
3. Drugs
Steroids: To lower inflammation for severe alcoholic hepatitis.
Experimental therapies meant to slow or reverse scarring are anti-fibrotic drugs.
4. Transplant of Liver
A liver transplant can be the sole life-saving choice for advanced cirrhosis. Eligibility for most transplant programs calls for at least six months of sobriety.
Advice on Preventing an Unhealthy Liver
Drink moderately or, preferably, skip alchealthy completely.
Keep a good weight to avoid fatty liver.
Vacúnate contra la hepatitis A y B.
Prevent hepatitis C by practicing safe sex and avoiding needle sharing.
If you have risk factors or drink frequently, regular check-ups will help you.
The Larger Picture: Alcohol’s Impact on World Health
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that alcohol causes well over three million fatalities per year, most of which are related to liver disease. Reducing this worldwide health load depends on increasing knowledge of the risks of too much drinking.
Ending
Every day your liver labors to maintain your health, but it is not unbreakable. Your liver could be harmed quietly but seriously by chronic alcohol misuse, which can cause diseases including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. The encouraging news? Early action—including eliminating alcohol and embracing a healthy lifestyle—can sometimes stop or reverse harm.

