Fatty Liver Disease in 84% of IT Workers: The Causes, Signs, and Prevention
Summary:
Overview
The concerning increase of fatty liver disease among IT workers
Why IT workers are more vulnerable
Knowledge of Fatty Liver Disease (FLD) H2
Fatty liver disease: what is it?
Fatty liver disease types: AFLD vs. NAFLD
What impact does it have on general health?
Why Do IT Workers Have a Higher Risk of Fatty Liver Disease?
Long periods of sitting and a sedentary lifestyle
Bad eating habits and a poor diet
Mental health problems and stress
Absence of exercise
Unusual schedules and disturbed sleep patterns
High intake of coffee and alcohol
IT Workers’ Signs of Fatty Liver Disease
Early indicators and quiet development
Typical signs to look out for
How it affects productivity at work
Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosis
Tests for liver function and blood
Imaging tests: MRI, FibroScan, and ultrasound
When is a liver biopsy required?
Fatty Liver Disease Treatment Options
Health Care Interventions
Prescription drugs
Tirzepatide and other weight-loss medications’ role
Changes in Lifestyle
The significance of dietary modifications
The benefits of exercise for liver health
Preventive Measures for IT Workers
Nutritious Food Practices
Foods to consume and foods to stay away from
The value of staying hydrated
Frequent Exercise
Easy activities for IT workers
Stretching and desk exercises
Stress Management and Mental Health
Meditation and mindfulness
The value of a healthy work-life balance
Enhancing Sleep Habits
The relationship between liver health and sleep
Advice for improved sleep hygiene
Initiatives for Workplace Wellness
Employers’ role in advancing health
Promoting exercise in the workplace
supplying cafeterias with healthier eating options
Summary
An overview of the main conclusions
Why liver health must be prioritized
Common Questions
Would it be possible to reverse fatty liver disease?
How long does it take for fatty liver disease to go away?
Which meals are most effective at reversing fatty liver?
Is fatty liver disease a result of stress alone?
If fatty liver disease is not treated, is it dangerous?
Fatty Liver Disease in 84% of IT Workers: The Causes, Signs, and Prevention
Overview
Did you know that fatty liver disease affects around 84% of IT workers? A growing health crisis in the tech sector is highlighted by this concerning number. Employees are particularly vulnerable to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) because of the modern IT work environment, which is characterized by lengthy sitting hours, high levels of stress, and bad eating habits. This essay examines the symptoms to watch for, the reasons why IT workers are more vulnerable, and practical strategies for preventing and treating this hidden but dangerous illness.
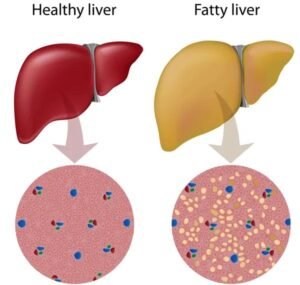
A Comprehensive Overview of Fatty Liver Disease (FLD)
Fatty liver disease: what is it?
When too much fat builds up in the liver, it can cause fatty liver disease. It is divided into two primary categories:
Obesity, metabolic problems, and poor lifestyle choices are the main causes of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): A condition brought on by consuming too much alcohol.
What Impact Does It Have on General Health?
Fatty liver can result in cirrhosis, liver fibrosis, and potentially liver cancer if treatment is not received. Diabetes, heart disease, and other metabolic diseases are also associated with it.
Why Do IT Workers Have a Higher Risk of Fatty Liver Disease?
Sedentary Lifestyle: Prolonged sitting slows down the metabolism and the burning of fat.
Unhealthy Diet: Excessive intake of processed foods, sugar, and junk food.
Prolonged stress raises cortisol levels, which encourage the liver to store fat.
Absence of exercise reduces insulin sensitivity, which causes fat to accumulate.
Alcohol and caffeine can impact the liver’s detoxification mechanisms.
Inadequate sleep patterns impair liver and metabolism.
IT Workers’ Signs of Fatty Liver Disease
Weakness and exhaustion
Unaccounted-for weight gain
Discomfort in the abdomen
Lack of focus and mental fog
Blood tests showing elevated liver enzymes
Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosis
Blood tests: Enzyme levels are checked using liver function tests.
Imaging tests: MRI, FibroScan, or ultrasound to measure liver fat.
In severe situations, a liver biopsy is necessary to identify cirrhosis or fibrosis.
Options for Fatty Liver Disease Treatment
Medical Interventions
prescription drugs to regulate metabolism.
Tirzepatide is one of the new medications that shows potential in lowering liver fat.
Changes in Lifestyle
Healthy Diet: Steer clear of processed meals, added sugars, and too many carbohydrates.
Exercise: Include both strength and cardio training.

Preventive Measures for IT Workers
Good Food Practices
Consume foods high in fiber and good fats.
Limit your consumption of processed foods and sweets.
Frequent Exercise
Stretch at your workstation and take a stroll during breaks.
Every day, try to get in at least 30 minutes of exercise.
Handling Sleep and Stress
Engage in deep breathing and meditation.
Keep a consistent sleep routine.
Initiatives for Workplace Wellness
Standing desks ought to be provided by employers.
Encourage healthy eating and exercise regimens.
In conclusion
Because of their lifestyle choices, IT workers are becoming increasingly concerned about fatty liver disease. However, the disease can be reversed and consequences avoided with minor dietary, exercise, and stress management adjustments. It’s time for IT workers to put their health and well-being first.
FAQs
Would it be possible to reverse fatty liver disease?
Yes, with dietary and exercise modifications.
How long does it take for fatty liver disease to go away?
In three to six months, mild instances can become better.
Which meals are most effective at reversing fatty liver?
Whole grains, fatty fish, leafy greens, and nuts.
Is fatty liver disease a result of stress alone?
Yes, indirectly. Stress has an impact on the liver and metabolism.
If fatty liver disease is not treated, is it dangerous?
Indeed, it can result in liver failure and cirrhosis.


1 thought on “Fatty Liver Disease in 84% of IT Workers-The Causes, Signs, and Prevention ”