Outline for the Article: A Comparison of the Use of Blood Products During Liver Transplantation
| Heading | Subheading |
|---|---|
| H1: Introduction | Overview of Liver Transplantation and Blood Product Usage |
| H2: Understanding Liver Transplantation | – Definition and Importance – Indications for Liver Transplantation |
| H2: Types of Blood Products Used | – Red Blood Cells – Platelets – Fresh Frozen Plasma – Cryoprecipitate |
| H2: Preoperative Considerations | – Assessing the Need for Blood Products – Patient Preparation |
| H2: Intraoperative Challenges | – Blood Loss During Liver Transplantation – Techniques to Minimize Blood Loss |
| H2: Role of Blood Product Transfusion | – Maintaining Hemodynamic Stability – Ensuring Coagulation Balance |
| H3: Techniques to Reduce Blood Product Usage | – Cell Salvage Systems – Antifibrinolytic Agents – Advanced Surgical Methods |
| H2: Postoperative Considerations | – Monitoring for Bleeding – Managing Transfusion-Related Complications |
| H2: Risks Associated with Blood Product Use | – Transfusion-Related Infections – Immunological Reactions |
| H2: Comparative Data on Blood Product Use | – Differences in Practices Across Institutions – Data from Retrospective and Prospective Studies |
| H3: Factors Influencing Blood Product Use | – Patient-Specific Factors – Institutional Protocols – Surgical Expertise |
| H2: Emerging Trends and Innovations | – Synthetic Blood Products – Role of Artificial Intelligence in Transfusion Management |
| H2: Ethical Considerations | – Ensuring Equitable Access to Blood Products – Addressing Scarcity Issues |
| H2: Recommendations for Optimized Practice | – Evidence-Based Guidelines – Training and Simulation Programs |
| H2: Conclusion | Summary of Key Findings and Implications for Practice |
| H2: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) | – Six detailed FAQs related to blood product use in liver transplantation |
A Comparison of the Use of Blood Products During Liver Transplantation
Overview
For patients with end-stage liver disease, liver transplantation is a life-saving treatment. It is also one of the most complicated surgeries, and in order to treat coagulation problems and hemodynamic stability, a lot of blood products are frequently needed. Insights into existing procedures, comparative statistics, and new developments are provided as this article explores the types, necessity, and difficulties of using blood products after liver transplantation.
Recognizing the Significance and Definition of In a liver transplant, a healthy donor organ is used to replace the diseased liver. For patients suffering from acute liver failure, liver cancer, or cirrhosis, it is essential.
Liver transplantation indications
Important signs consist of:
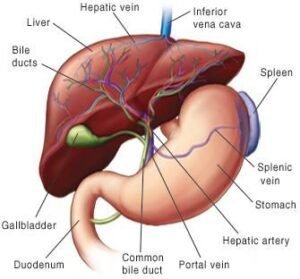
Chronic liver disease, such as alcohol-induced cirrhosis and hepatitis
Acute liver failure
Hepatocellular carcinoma in the context of transplant requirements
Liver diseases caused by genetics
Blood Product Types Red blood cells (RBCs) in use
RBC infusions guarantee oxygen supply during surgery and treat anemia.
Particularly in individuals with low platelet counts prior to surgery, platelets are essential for preventing severe bleeding.
Frozen Plasma Fresh (FFP)
Clotting factors, which are essential for treating coagulopathy, are provided by FFP.
The cryoprecipitate
Cryoprecipitate, which is high in fibrinogen, is necessary for the development of clots in individuals with severe coagulopathy.
Preoperative Considerations for Evaluating Blood Product Needs
To anticipate any blood loss, patients go through thorough preoperative assessments.
Getting the Patient Ready
Important preoperative measures include maximizing hemoglobin levels, addressing coagulation disorders, and guaranteeing vascular access.
Intraoperative Difficulties
During liver transplantation, blood loss occurs.
Because of the vascular structure of the liver, significant blood loss is frequent and requires careful planning.
Methods to Reduce Blood Loss
Cutting-edge surgical techniques that lessen intraoperative bleeding include topical hemostatic medications and vascular clamping.
The function of transfusion of blood products
Blood products are necessary to handle large transfusions during liver transplantation, maintain hemodynamic stability, and treat clotting problems.

Methods for Cutting Down on the Use of Blood Products
Systems for Cell Salvage
By recovering and recycling the patient’s blood, these devices lessen the need for donor blood.
Agents that inhibit fibrinolysis
Tranexamic acid is one medication that reduces bleeding by preventing clots from breaking down.
Advanced Techniques in Surgery
Less blood is lost with robotic assistance and laparoscopic procedures.
Considerations After Surgery
Keeping an eye out for bleeding
Timely intervention for postoperative bleeding is ensured by close monitoring.
Handling Complications Associated with Transfusions
It’s crucial to recognize and address issues like transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI).
Hazards Associated with the Use of Blood Products: These hazards include:
Infections (such as HIV and hepatitis)
Immunological responses, such as hemolytic responses
Comparative Data on Blood Product Consumption Studies show that surgical skill, patient characteristics, and procedures all have an impact on the considerable difference in blood product consumption throughout institutions.
New Developments and Trends
Products Made with Synthetic Blood
The goal of artificial blood advancements is to address the scarcity of donor blood.
Artificial Intelligence’s Function
Predictive methods powered by AI optimize transfusion tactics, cutting waste and enhancing results.
Moral Aspects to Take into Account
Addressing scarcity in environments with limited resources and guaranteeing fair access to blood products are examples of ethical challenges.
Suggestions for the Best Practice
Improving liver transplant results requires interdisciplinary cooperation, simulated training, and evidence-based recommendations.
Questions and Answers (FAQs)
Why do liver transplants require the use of blood products?
Throughout surgery, blood products control coagulation issues and preserve hemodynamic stability.
What dangers come with receiving blood transfusions?
Immune suppression, allergic reactions, and infections are among the risks.
How does a liver transplant limit blood loss?
Blood loss is decreased by strategies like cell salvage, antifibrinolytics, and sophisticated surgical techniques.
Are items made from synthetic blood effective?
Synthetic blood is currently in the experimental stage, but it has the potential to lessen dependency on donor supplies.
What are the typical side effects of receiving blood transfusions?
Hemolytic responses, iron overload, and TRALI are among the complications.
How do different institutions use blood products?
Disparities result from institutional procedures, surgical skill, and patient demographics.

